How to make money in Natural Gas with Excel
Posted: 2023-10-20

One of the strategies is to buy cheap summer gas, store it for few months, and sell as expensive winter gas. Easily said than done. But how much should you pay for the storage facility and how to hedge the risk?
In this post we are going to review a simple gas storage model with static replication. This is an educational exercise and it is designed for simplicity.
Natural Gas storage is a critical function that operators use to balance the demand and supply especially during summer / winter seasons. Historically the heating demand for Natural Gas during winter is much higher than summer power burn and industrial demand which is reflected in the gas forward curve.

As mentioned earlier, winter Natural Gas demand is typically higher than available supply hence winter prices are also typically higher than summer prices. Gas storage owners use this phenomenon to buy “cheap” gas during summer months and sell during more expensive winter months.
Let us look at a simple storage model with 1y firm contract with no ratchets, no injection, draw and financing costs and no bid-offer or locational spreads. The hedge will follow static replication method, which means we are not taking volatility into consideration just price levels.
To solve optimization problem, we need to first define a target function. We are going to maximize revenue by buying gas and selling it later. The schedule will be subject to constraints: - maximum storage level cannot be greater than 100,000 dekatherms - maximum daily injection rate cannot be greater than 2,000 dekatherms - maximum daily withdrawal rate cannot be greater than 4,000 dekatherms
This formula describes our target function: $$ \max \sum Q{ij}(P{j}-P{i}) $$ , where: $Q{ij}$ means we are buying $Q$ dekatherms in month $i$, keeping it in storage and selling the same amount in month $j$. $P{i}$ and $P{j}$ are respective purchase and sell prices.
We are going to skip constraints for brevity, the target formula and constraints are implemented in attached Excel sheet.
Using Excel solver shows that we can make revenue of USD 39,520 so if storage costs less than that we can make some profit.
Here is calculated hedging plan. For example, we need to buy 3 April’21 contracts at price 2.921 and sell 3 Jan’22 contracts at price 3.294 to hedge the P&L.
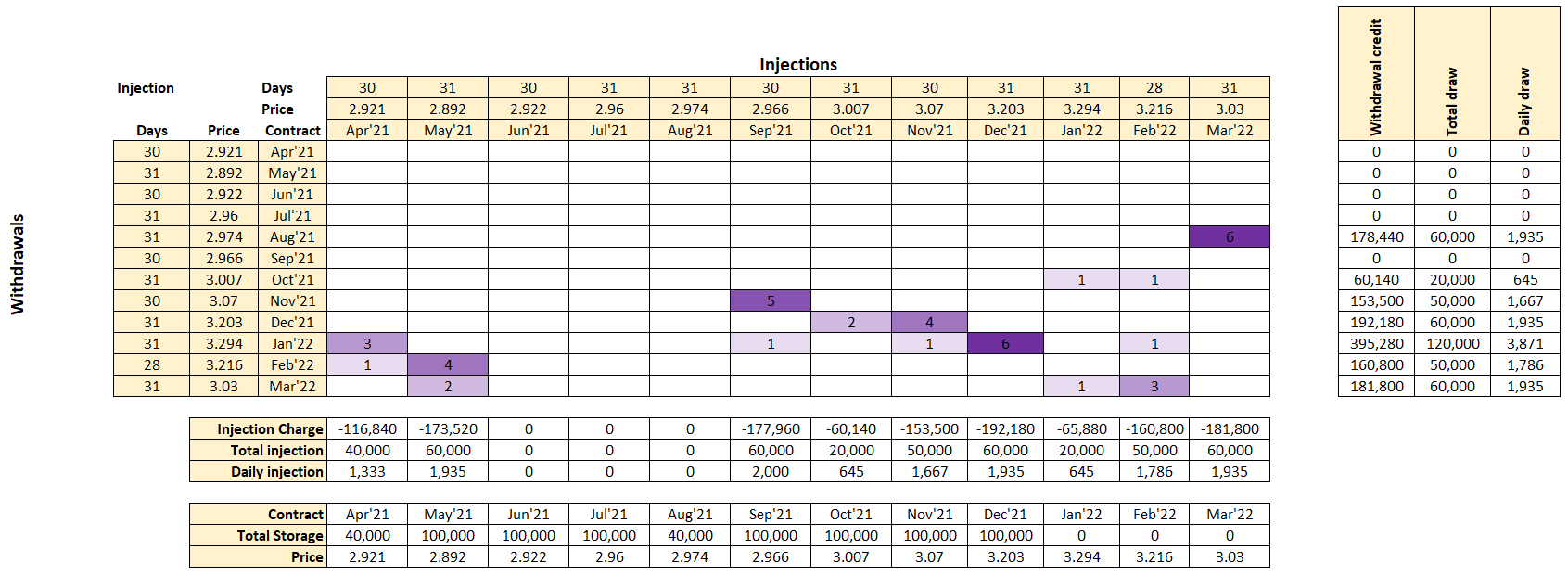
This chart shows amount of gas in storage for calculated plan vs the forward prices. The solver did an excellent job and constrained maximum storage level to 100,000 as was required.
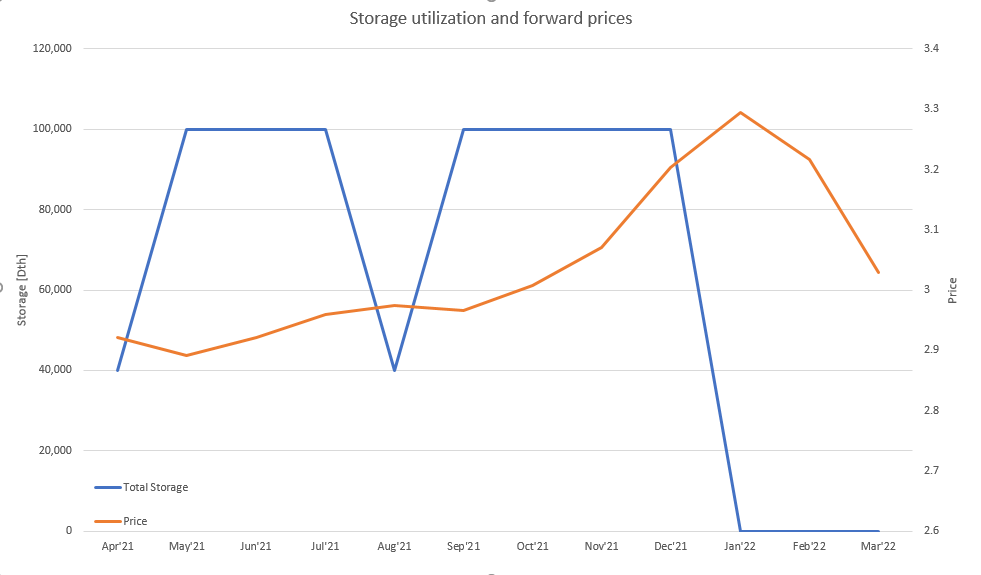
Photo by Josh Appel on Unsplash